Life On Mars Search Could Be Misled By False Fossils, Study Says
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – Mars explorers searching for signs of ancient life could be fooled by fossil-like specimens created by chemical processes, research suggests.
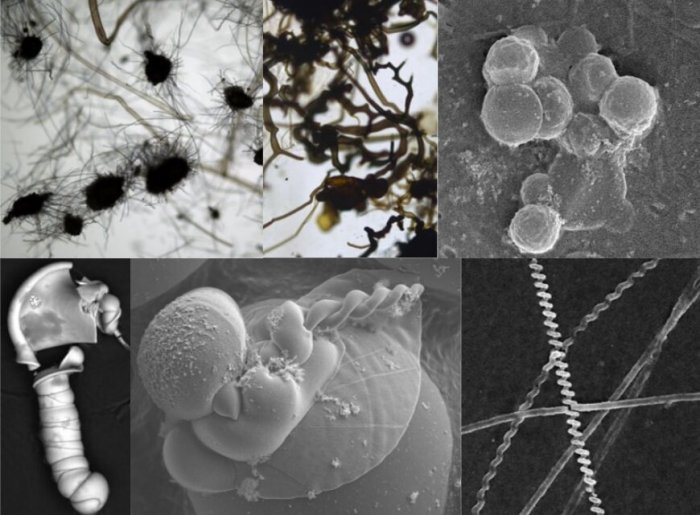
Composite image showing some of the types of fossil-like specimens created by chemical reactions that could be found on Mars. Credit: Sean McMahon, Julie Cosmidis and Joti Rouillard
Telling these false fossils apart from what could be evidence of ancient life on the surface of Mars—which was temporarily habitable four billion years ago—is key to the success of current and future missions, researchers say.
Astrobiologists from the Universities of Edinburgh and Oxford reviewed evidence of all known processes that could have created lifelike deposits in rocks on Mars.
They identified dozens of processes—with many more likely still undiscovered—that can produce structures that mimic those of microscopic, simple lifeforms that may once have existed on Mars.
Among the lifelike specimens, these processes can create are deposits that look like bacterial cells and carbon-based molecules that closely resemble the building blocks of all known life.
Because signs of life can be so closely mimicked by non-living processes, the origins of any fossil-like specimens found on Mars are likely to be very ambiguous, the team says.
They call for greater interdisciplinary research to shed more light on how lifelike deposits could form on Mars, and thereby aid the search for evidence of ancient life there and elsewhere in the solar system.
The research is published in the Journal of the Geological Society.
Dr. Sean McMahon, Chancellor’s Fellow in Astrobiology at the University of Edinburgh’s School of Physic and Astronomy, said: “At some stage a Mars rover will almost certainly find something that looks a lot like a fossil, so being able to confidently distinguish these from structures and substances made by chemical reactions is vital.
For every type of fossil out there, there is at least one non-biological process that creates very similar things, so there is a real need to improve our understanding of how these form.”
Julie Cosmidis, Associate Professor of Geobiology at the University of Oxford, said: “We have been fooled by life-mimicking processes in the past. On many occasions, objects that looked like fossil microbes were described in ancient rocks on Earth and even in meteorites from Mars, but after deeper examination they turned out to have non-biological origins.
This article is a cautionary tale in which we call for further research on life-mimicking processes in the context of Mars, so that we avoid falling into the same traps over and over again.”
Study published in Journal of the Geological Society, 2021; jgs2021-050 DOI: 10.1144/jgs2021-050
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. MessageToEagle.com Staff