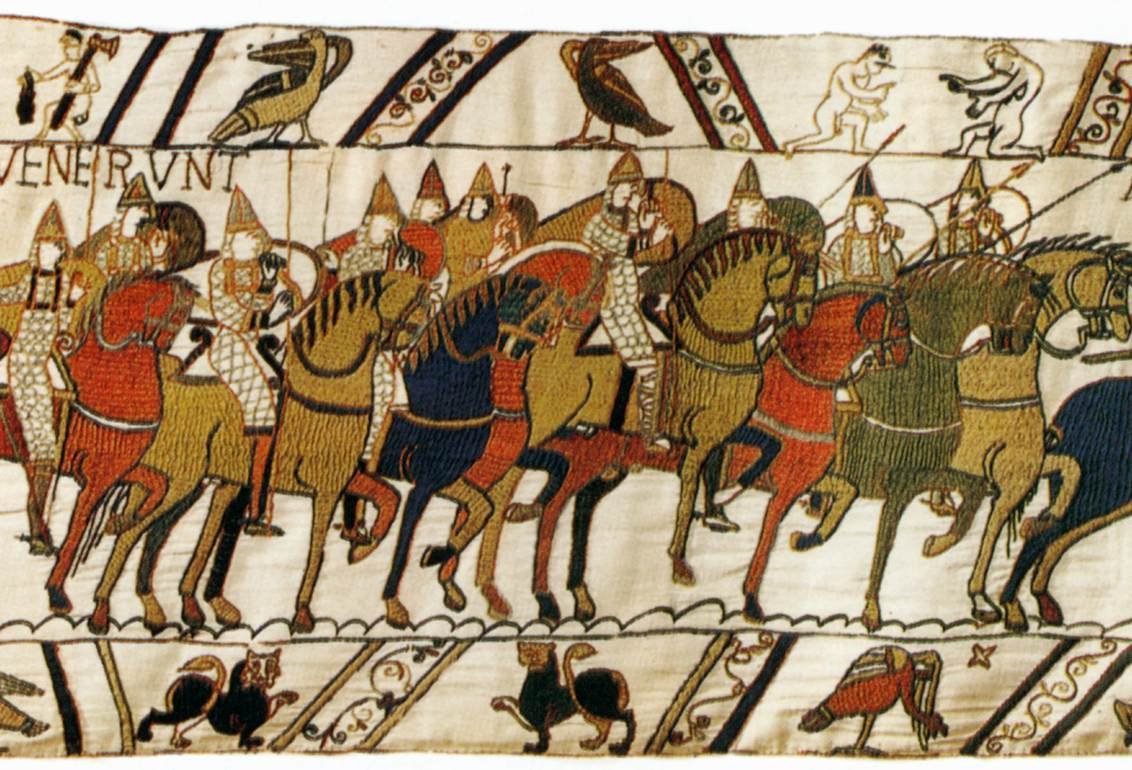
The Bayeux Tapestry: One Of The Great Historical Records Of The Middle Ages
A. Sutherland – MessageToEagle.com – The Bayeux Tapestry is an impressive example of Romanesque art depicting the Norman Conquest of England in 1066 by William, duke of Normandy, the historical event that culminated in the famous Battle of Hastings (Oct. 14, 1066).
The Bayeux Tapestry’s vivid action expressed in the scenes strongly resembles a film, but it is more than that; the artifact is important as a source for 11th-century history.
When first referred to (1476), the tapestry was used once a year to decorate the nave of the cathedral in Bayeux, France. There it was “discovered” by the French antiquarian and scholar Bernard de Montfaucon, who published the earliest complete reproduction of it in 1730.
The artwork – made in England, in the 1070s – is an embroidered cloth, about 229 feet (70m), 19.5 inches (49.5 cm) wide and weighs 350 kilos. It consists of fifty-eight embroidered scenes (other sources mention more than 70 scenes) with Latin tituli, embroidered on linen with colored woollen yarns.
With few exceptions, the events are presented in the historically correct sequence, with each of the heroes appearing several times.
Having twice narrowly escaped destruction during the French Revolution, the tapestry was exhibited in Paris at Napoleon’s wish in 1803–04 and thereafter was in civil custody at Bayeux, except in 1871 (during the Franco-German War) and from September 1939 to March 1945 (during World War II).
The borders on the tapestry are full of additional depictions of subplots and legends that constitute a complement to the main scenes.
Towards the end, the vivid action of the Battle of Hastings culminates and the lower border of the tapestry is devoted to dead and wounded soldiers, hordes of bowmen, and the plundering of casualties.
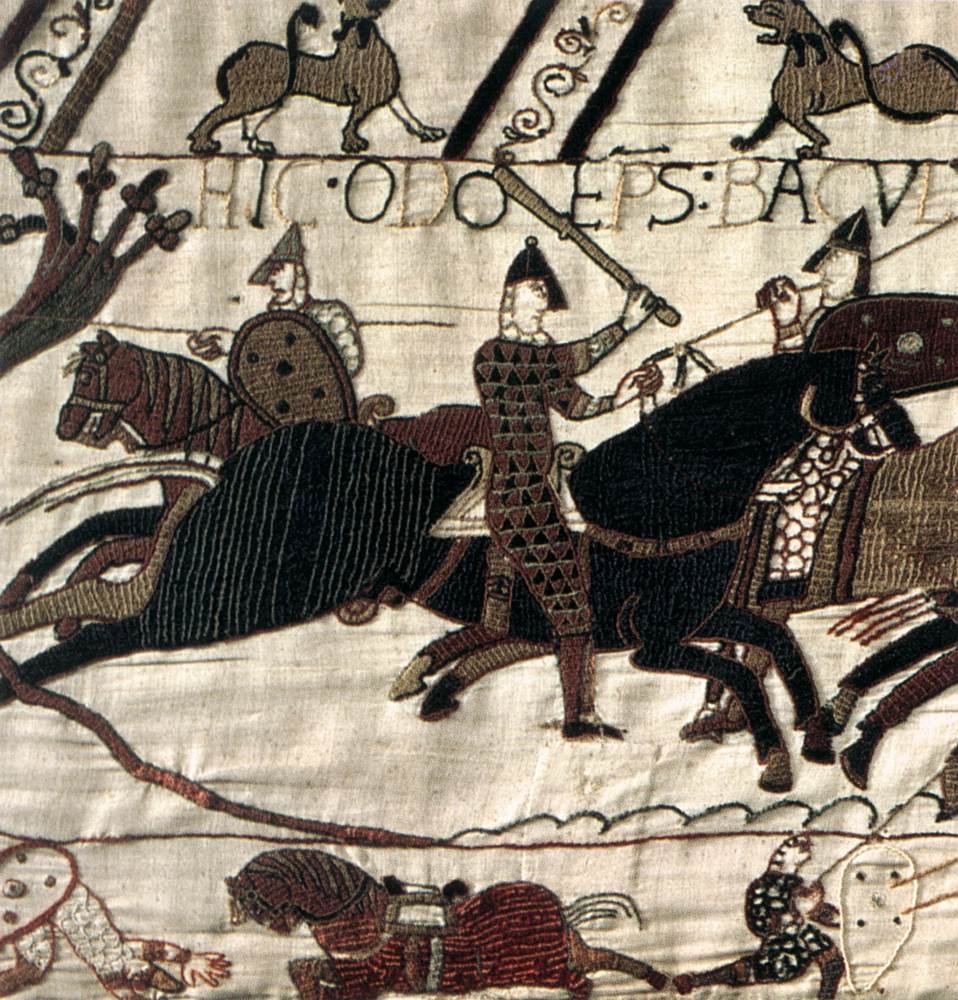

It is easy to imagine all these events because an unknown skilled artist – an unknown English weaver – narrates them visually, leading the eye from one phase to another.
The depictions on the Bayeux Tapestry are handmade with woollen threads and needled onto a strip of linen. They are embroidered in red, yellow, grey, bright green and a darker green, and three shades of blue.
Although the tapestry has been exposed to light and dirt for over nine centuries, the eight colors of woollen thread are still vivid, bright and beautiful.
Many art historians assume that the tapestry was made in southern England (perhaps at the St Augustine monastery in Canterbury) for Odo of Bayeux, bishop and half-brother of William the Conqueror. Almost certainly, the tapestry was hung in the hall of a bishop’s palace.
It is presently exhibited in a special museum in Bayeux, Normandy, France, with a Victorian replica in Reading, Berkshire, England.
Written by – A. Sutherland – MessageToEagle.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © MessageToeagle.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of MessageToeagle.com
Expand for referencessource: Britannica
Related Posts
-
 Large Palace Discovered At Mayan City Of Kulubá In Yucatan, Mexico
No Comments | Dec 29, 2019
Large Palace Discovered At Mayan City Of Kulubá In Yucatan, Mexico
No Comments | Dec 29, 2019 -
 Mysterious Giant Footprints In China: Evidence That Huge Humans Roamed The Earth?
No Comments | Feb 28, 2017
Mysterious Giant Footprints In China: Evidence That Huge Humans Roamed The Earth?
No Comments | Feb 28, 2017 -
 Extraterrestrial Visit Recorded On Stone: They Came From The Stars
No Comments | May 4, 2014
Extraterrestrial Visit Recorded On Stone: They Came From The Stars
No Comments | May 4, 2014 -
 Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
No Comments | Mar 3, 2021
Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
No Comments | Mar 3, 2021 -
 New Controversial Evidence – Ancient Chinese Visited America 2,500 Years Ago
No Comments | May 9, 2015
New Controversial Evidence – Ancient Chinese Visited America 2,500 Years Ago
No Comments | May 9, 2015 -
 Artificial And Extraterrestrial Interference In The Development Of The Human Race
No Comments | May 6, 2015
Artificial And Extraterrestrial Interference In The Development Of The Human Race
No Comments | May 6, 2015 -
 Shepherd’s Monument Mystery: Yet Another Undeciphered Inscription
No Comments | Jan 27, 2015
Shepherd’s Monument Mystery: Yet Another Undeciphered Inscription
No Comments | Jan 27, 2015 -
 Striking Hindu Temples – Maya And Sumer Connection
No Comments | Jan 25, 2015
Striking Hindu Temples – Maya And Sumer Connection
No Comments | Jan 25, 2015 -
 Surprising Discovery – Replica In The Field Museum Is A 3,000-Year-Old Sword
No Comments | Jan 20, 2023
Surprising Discovery – Replica In The Field Museum Is A 3,000-Year-Old Sword
No Comments | Jan 20, 2023 -
 Mystery Of The Gotland Grooves – Ancient Astronomical Observatory?
No Comments | Mar 11, 2016
Mystery Of The Gotland Grooves – Ancient Astronomical Observatory?
No Comments | Mar 11, 2016


