Aging Stellar Goliath VY Canis Majoris Caught In Act Of Slimming Down
MessageToEagle.com – A team of astronomers using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) has captured the most detailed images ever of the hypergiant star VY Canis Majoris. These observations show how the unexpectedly large size of the particles of dust surrounding the star enable it to lose an enormous amount of mass as it begins to die.
This process is necessary to prepare such gigantic stars to meet explosive demises as supernovae.
- VY Canis Majoris is a stellar goliath, a red hypergiant, one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way.
- It is 30–40 times the mass of the Sun and 300 000 times more luminous. In its current state, the star would encompass the orbit of Jupiter, having expanded tremendously as it enters the final stages of its life.
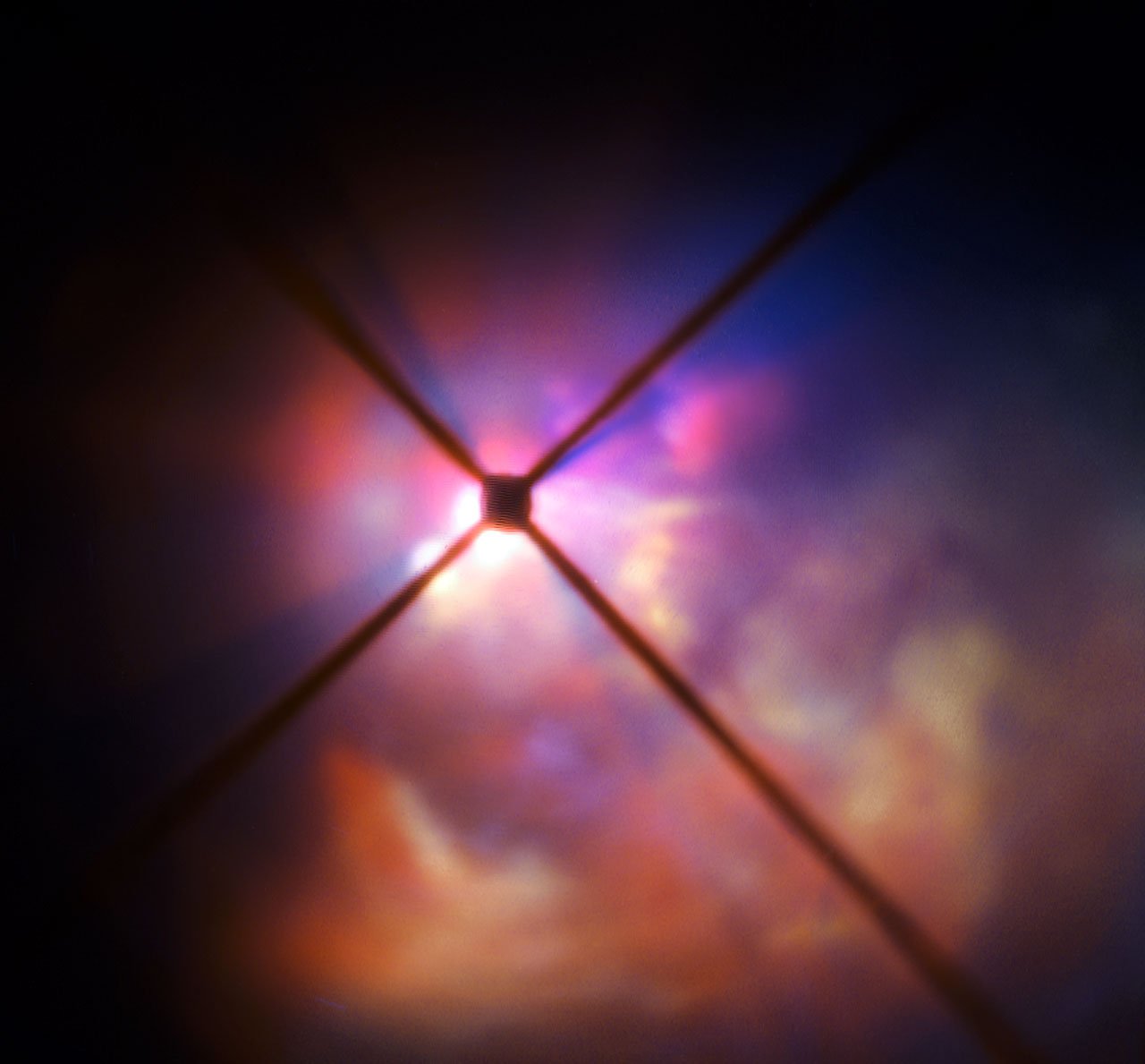

Astronomers used the SPHERE instrument on the VLT to observe the star. The SPHERE clearly revealed how the brilliant light of VY Canis Majoris was lighting up clouds of material surrounding it.
The team could also see how the starlight was scattered and polarised by the surrounding material. These measurements were key to discovering the elusive properties of the dust.
Also analysis of the polarisation results revealed these grains of dust to be comparatively large particles, 0.5 micrometres across, which may seem small, but grains of this size are about 50 times larger than the dust normally found in interstellar space.

Until now, it had remained mysterious how the material in these giant stars’ upper atmospheres is pushed away into space before the host explodes. The most likely driver has always seemed to be radiation pressure, the force that starlight exerts.
As this pressure is very weak, the process relies on large grains of dust, to ensure a broad enough surface area to have an appreciable effect.
“Massive stars live short lives,” says lead author of the paper, Peter Scicluna, of the Academia Sinica Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics, Taiwan.
“When they near their final days, they lose a lot of mass. In the past, we could only theorise about how this happened. But now, with the new SPHERE data, we have found large grains of dust around this hypergiant. These are big enough to be pushed away by the star’s intense radiation pressure, which explains the star’s rapid mass loss.”
The large grains of dust observed so close to the star mean that the cloud can effectively scatter the star’s visible light and be pushed by the radiation pressure from the star.
The size of the dust grains also means much of it is likely to survive the radiation produced by VY Canis Majoris’ inevitable dramatic demise as a supernova. This dust then contributes to the surrounding interstellar medium, feeding future generations of stars and encouraging them to form planets.
MessageToEagle.com
via ESO










