World’s Oldest Evidence Of Man-Made Climate Change Discovered In 11,500-Year-Old Samples From Dead Sea
MessageToEagle.com – As the climate change debate continues, many keep asking – who is responsible for climate-warming trends over the past century? Should we blame humans, Mother Nature or a combination of both?
The vast majority of climate scientists seems to agree that human activities are changing our climate in a devastating way.
Researchers report they have discovered world’s oldest evidence, suggesting man-made climate change took place 11,500 years ago, during the Neolithic Revolution.
By examining a core sample retrieved from the Dead Sea, researchers discovered basin-wide erosion rates dramatically incompatible with known tectonic and climatic regimes of the period recorded.
The results of the study were published in Global and Planetary Change.
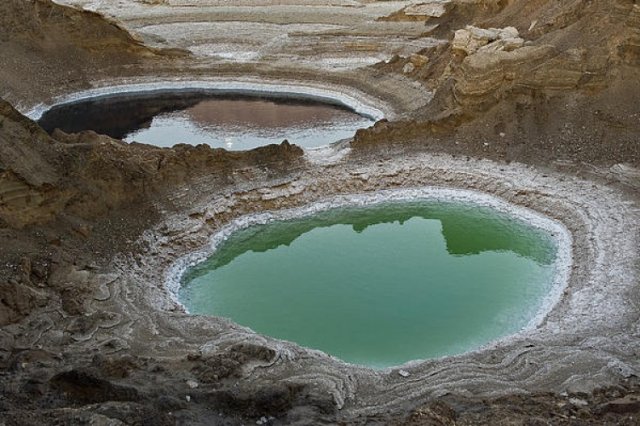

The research was part of the Dead Sea Deep Drilling project, which harnessed a 1,500-foot-deep drill core to delve into the Dead Sea basin. The core sample provided the team with a sediment record of the last 220,000 years.
According to scientists, the newly-discovered erosion occurred during the Neolithic Revolution, the wide-scale transition of human cultures from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. The shift resulted in an exponentially larger human population on the planet.
The Dead Sea drainage basin serves as a natural laboratory for understanding how sedimentation rates in a deep basin are related to climate change, tectonics, and man-made impacts on the landscape.
See also:
The Dead Sea Reveals Evidence Of Ancient Climate Change And A Warning For The Future
What Changed The Green Sahara Into A Desert?
Evidence Climate Change Caused Global Mass Extinction 30,000 Years Ago
“Human impact on the natural environment is now endangering the entire planet,” said Professor Shmuel Marco, Head of TAU’s School of Geosciences, who led the research team.
“It is therefore crucial to understand these fundamental processes. Our discovery provides a quantitative assessment for the commencement of significant human impact on the Earth’s geology and ecosystems.

Natural vegetation was replaced by crops, animals were domesticated, grazing reduced the natural plant cover, and deforestation provided more area for grazing
All these resulted in the intensified erosion of the surface and increased sedimentation, which we discovered in the Dead Sea core sample.”
Researchers explain they noted a sharp threefold increase in the fine sand that was carried into the Dead Sea by seasonal floods.
“This intensified erosion is incompatible with tectonic and climatic regimes during the Holocene, the geological epoch that began after the Pleistocene some 11,700 years ago,” Professor Marco said.
The researchers are currently in the process of recovering the record of earthquakes from the same drill core. “We have identified disturbances in the sediment layers that were triggered by the shaking of the lake bottom,” Prof. Marco said. “It will provide us with a 220,000-year record — the most extensive earthquake record in the world.”
MessageToEagle.com
Expand for references