Evidence Of Cataclysmic Flare That Exploded 3.5 Million Years Ago
Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com – A titanic, expanding beam of energy sprang from close to the supermassive black hole in the center of the Milky Way just 3.5 million years ago, sending a cone-shaped burst of radiation through both poles of the Galaxy and out into deep space.
The phenomenon, known as a Seyfert flare, created two enormous ‘ionization cones’ that sliced through the Milky Way – beginning with a relatively small diameter close to the black hole, and expanding vastly as they exited the Galaxy.
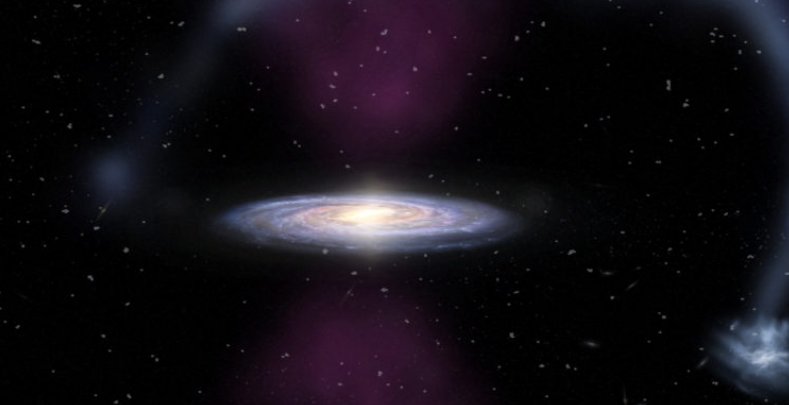 An artist’s impression of the massive bursts of ionising radiation exploding from the centre of the Milky Way and impacting the Magellanic Stream. Credit: James Josephides/Thorsten Tepper-Garcia/ASTRO 3D
An artist’s impression of the massive bursts of ionising radiation exploding from the centre of the Milky Way and impacting the Magellanic Stream. Credit: James Josephides/Thorsten Tepper-Garcia/ASTRO 3D
So powerful was the flare that it impacted on the Magellanic Stream – a long trail of gas extending from nearby dwarf galaxies called the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. The Magellanic Stream lies at an average 200,000 light-years from the Milky Way.
The explosion was too huge, says the Australian-US research team, to have been triggered by anything other than nuclear activity associated with the black hole, known as Sagittarius A, or Sgr A*, which is about 4.2 million times more massive than the Sun.
“The flare must have been a bit like a lighthouse beam,” Professor Joss Bland-Hawthorn, from Australia’s ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics at the University of Sydney, said in a press release.
“Imagine darkness, and then someone switches on a lighthouse beacon for a brief period of time.”
Using data gathered by the Hubble Space Telescope, the researchers calculated that the massive explosion took place little more than three million years ago.
In Galactic terms, that is astonishingly recent. On Earth at that point, the asteroid that triggered the extinction of the dinosaurs was already 63 million years in the past, and humanity’s ancient ancestors, the Australopithecines, were afoot in Africa.
The paper follows on from research also led by Professor Bland-Hawthorn and published in 2013. The earlier work looked at evidence of a massive explosive event beginning in the center of the Milky Way, ruled out a nuclear starburst as the cause and tentatively tied it to activity in SgrA*.
Written by Eddie Gonzales Jr. – MessageToEagle.com Staff