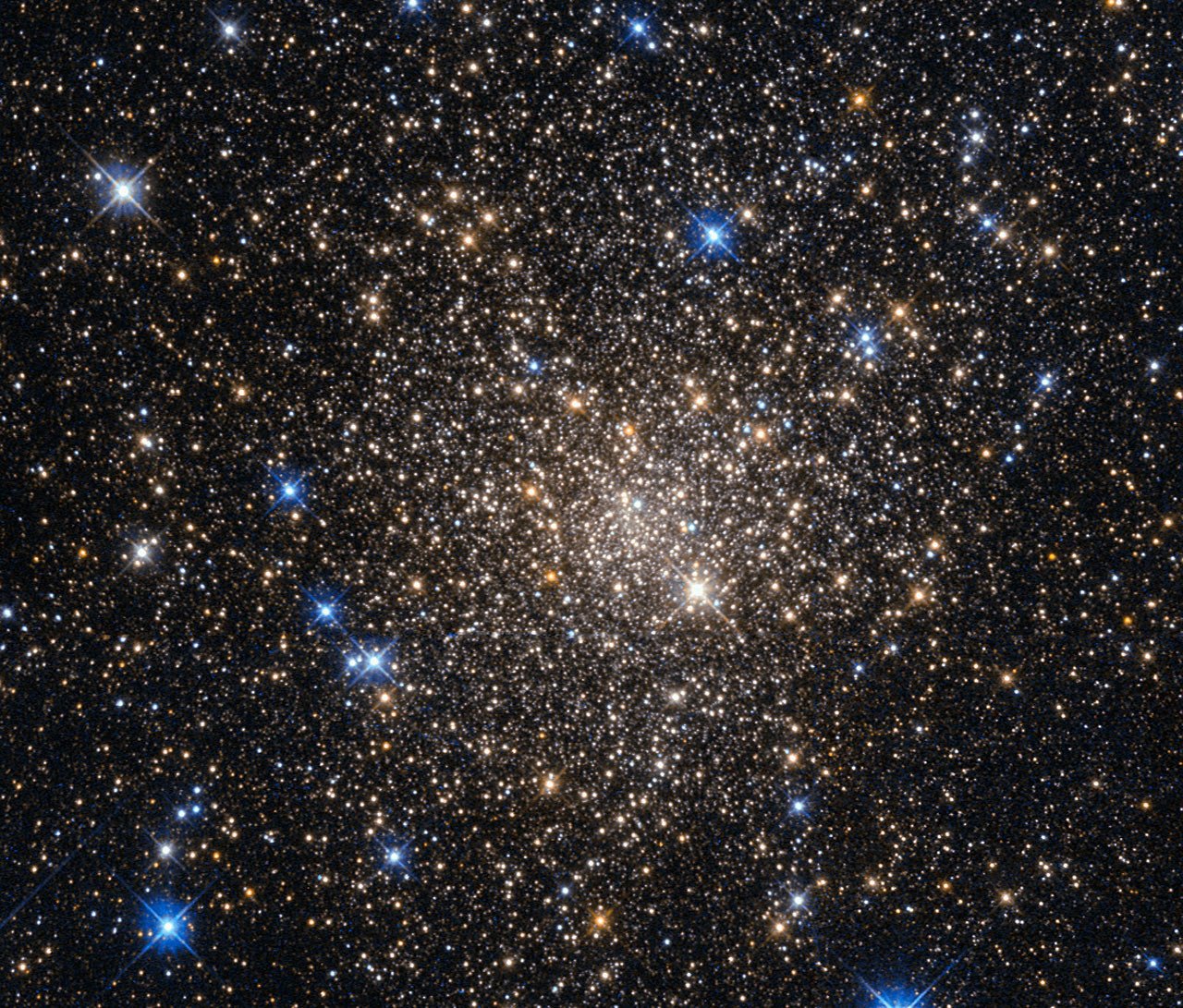
Hubble Presents Terzan 1: A Home For Old Stars In The Constellation Of Scorpius
MessageToEagle.com – The Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the globular cluster Terzan 1.
Terzan 1 is located approximately 20,000 light-years from us in the constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion) and it is one of about 150 globular clusters belonging to our galaxy, the Milky Way.
- Globular clusters are spherical concentrations of stars typically 100 light years across and containing thousands of stars held together by their mutual gravitational attraction in a spherical shape a few hundred light-years across.

- Globular clusters are very old, at least 10 billion years old and were presumably formed when the galaxy was still forming.
- They are scattered in a spherical halo surrounding our galaxy and they require hundreds of millions of years to orbit it.
It is thought that every galaxy has a population of globular clusters. Some, like the Milky Way, have a few hundred, while giant elliptical galaxies can have several thousand.
They contain some of the oldest stars in a galaxy, hence the reddish colors of the stars in this image — the bright blue ones are foreground stars, not part of the cluster. The ages of the stars in the globular cluster tell us that they were formed during the early stages of galaxy formation!
Studying them can also help us to understand how galaxies formed.
Terzan 1, like many globular clusters, is a source of X-rays. It is likely that these X-rays come from binary star systems that contain a dense neutron star and a normal star. The neutron star drags material from the companion star, causing a burst of X-ray emission.
The system then enters a quiescent phase in which the neutron star cools, giving off X-ray emission with different characteristics, before enough material from the companion builds up to trigger another outburst.
MessageToEagle.com
via NASA